- 2094, Dividing Rd, Phase 2, Urban Estate Dugri, Ludhiana
- +91 8872036060
- harpaldr@yahoo.com
LIVER CLINIC
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver, most commonly caused by a viral infection. There are five viruses that cause the disease: Hepatitis A, B, C, D and E. Types B and C lead to chronic disease in hundreds of millions of people and, together, are the most common cause of liver cirrhosis and cancer.
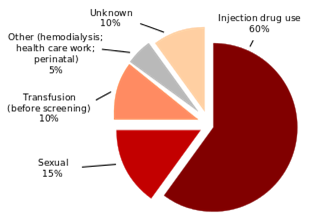
Hepatitis C, a leading cause of chronic liver disease globally, is caused by Hepatitis C Virus (HCV), a hepatotropic RNA virus. HCV infection starts with an acute infection, mostly subclinical, which ultimately leads to chronic hepatitis in about 80% of the infected cases. Genotype 1 is the most common worldwide, Genotype 3 is the commonest genotype in India.
Hepatitis Facts
- About 150 million people are chronically infected with hepatitis C virus, and more than 350, 000 people die every year from hepatitis C-related liver diseases across the world
- Hepatitis C IS TREATABLE WITH medicines
- There is currently no vaccine for hepatitis C; research is on
- Unnecessary and unsafe injections
- Unsafe blood products
- Unsafe waste collection and disposal
- Use of illicit drugs and sharing of injection equipment
- Unprotected sex with hepatitis C-infected people
- Sharing of sharp-edged personal items like razors that may be contaminated with infected blood
- Tattoos, piercing and acupuncture performed with contaminated equipment
Risk of infection can be reduced by avoiding:
Hhepatitis A and E are typically caused by ingestion of contaminated food or water. Hepatitis B, C and D usually occur as a result of parenteral contact with infected body fluids.
Treatment With the introduction of new oral drugs, the Directly Acting Antivirals (DAA), the management protocols of hepatitis C has undergone dramatic transformation. However, developing countries like India still face a challenge with respect to accessibility and affordability of such newer regimens. Furthermore, the differences in genotypic distributions in India, with a higher prevalence of genotype 3, which is more difficult to treat, makes the situation even more challenging.
Liver Cancer
Liver is the organ which is situated in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen. The size of a football, it is located beneath the diaphragm and above the stomach. Cancer of the liver or liver cancer starts from the main cell of the liver, which is the hepatocyte. Liver cancer is also called hepatocellular carcinoma.
What Causes Liver Cancer?- Chronic infection such as hepatitis B and C
- Hemochromatosis – this is a hereditary disease with too much iron contained in the liver
- Cirrhosis – scarring condition of the liver due to alcohol abuse
- Obesity
- Alcohol abuse
- Herbicides and chemicals such as vinyl chloride and arsenic
- Aflatoxins – these usually contaminate foods such as rice, wheat, corn and peanuts
- Androgen and estrogen hormonal conditions
- Initially asymptomatic
- Yellow discoloration of eyes and skin: jaundice
- Itching caused by jaundice
- Chalky stools
- Upper abdominal pain in the liver area
- Loss of appetite
- Loss of weight
- Fatigue and weakness
- Abdominal swelling – due to the growing cancer or accumulation of fluid
Liver cancer if detected early can be cured. Various options are available depending upon the stage of the cancer and underlying liver condition. I t includes liver resection, radio frequency ablation, tranarterial treatment such as TACE or TARE. In advanced liver disease , liver transplant is the mainstay of treatment.